If you’ve ever wondered how to increase metabolism, you’re not alone. Metabolism is your body’s engine. It turns food into the energy you need to move, think, and live. When your metabolism runs efficiently, you tend to feel better, have more energy, and maintain a healthier weight. But what exactly influences your metabolic rate? And how do you keep it in top shape?
In this guide, we’ll explore the fundamentals of metabolism and uncover simple steps you can take to support it. We’ll discuss metabolism-boosting foods and drinks, the importance of muscle mass, and how daily habits like sleep and stress management impact your body’s energy use. You’ll see that making small changes—like following a balanced diet or finding ways to manage cortisol—can make a big difference. By the end, you’ll be equipped with proven strategies and fresh perspectives to naturally support and increase your metabolic rate. Let’s get started.
1. Metabolism Basics—What It Is and Why It Matters
Metabolism is the set of chemical processes that occur in your body to maintain life. It’s how you convert what you eat and drink into energy. This energy fuels everything from thinking to breathing. It even helps keep your heart beating. Knowing how to increase metabolism starts with understanding what it really is.
Your metabolic rate (the speed of your metabolism) depends on factors like age, genetics, body composition, and gender. The body burns calories at rest to support essential functions—this is called your basal metabolic rate (BMR). Any physical activity you do, whether it’s a morning walk or a HIIT workout, increases how many calories you burn in a day. Even the process of digesting food (the thermic effect of food, or TEF) boosts calorie expenditure slightly.
The key takeaway is that metabolism is dynamic. When you have more lean muscle mass, you tend to burn more calories even when you’re sitting still. When your body composition is higher in body fat, your metabolic rate can be slower. For those looking for ways to naturally boost metabolism, focusing on lean muscle building can pay off in the long run. Additionally, managing stress for metabolism is important, because chronic stress can disrupt normal metabolic processes by altering hormone levels, including cortisol.
One lesser-discussed factor is magnesium glycinate supplementation. Magnesium supports over 300 biochemical reactions, including those tied to metabolic function (Healthline, 2022). While research is still expanding in this area, some experts believe maintaining adequate magnesium levels may keep metabolism functioning more smoothly. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods (like leafy greens or nuts) might also be beneficial.
2. The Role of Nutrition—Fueling a Healthy Metabolism
A balanced diet is the cornerstone of a healthy metabolism. If you’re aiming to learn how to increase metabolism through food alone, pay attention to quality just as much as quantity. It’s true that calories matter. But what those calories contain can change how your body processes them.
Focus on Protein Intake
Protein not only helps with muscle repair and growth but also has a thermic effect. This means your body burns more calories digesting protein compared to carbohydrates or fats (Medical News Today, 2021). Incorporating lean protein sources like chicken, fish, beans, or lentils can be part of your strategy for increasing metabolism safely.
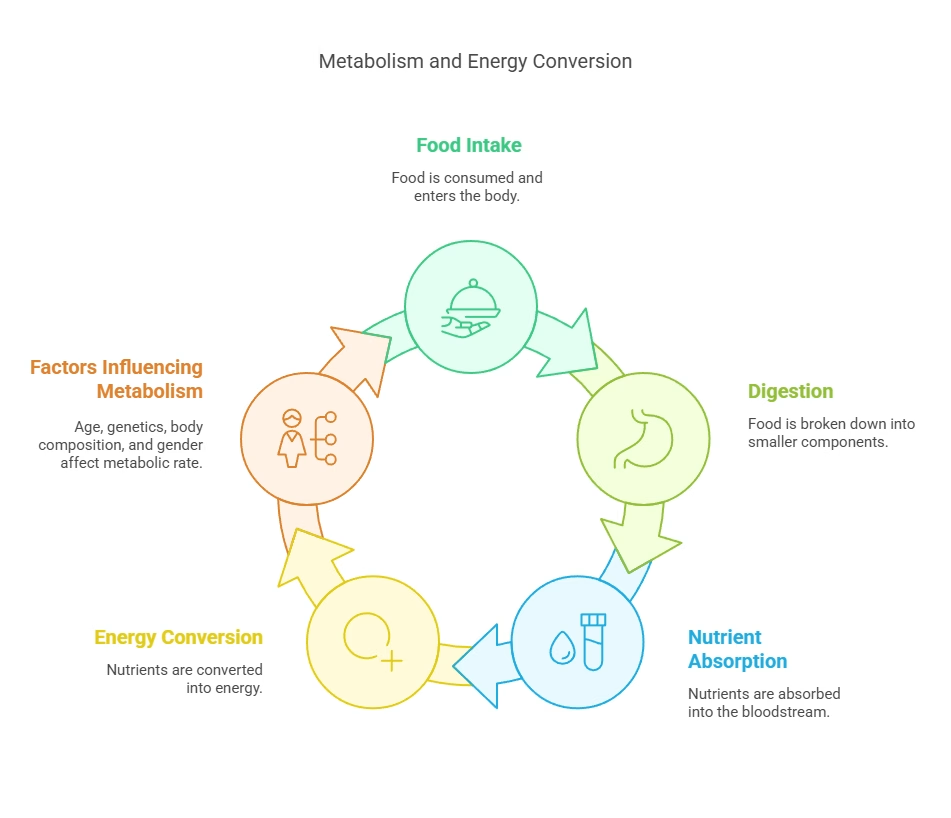
Embrace Metabolism-Boosting Foods and Drinks
Foods like chili peppers, ginger, and green tea may give a slight metabolic lift. While these aren’t magic bullets, research suggests that active compounds like capsaicin (in chili peppers) and catechins (in green tea) can boost calorie expenditure to some degree (Everyday Health, 2021). If you enjoy a bit of heat, sprinkling some chili flakes over your meal might be a fun experiment.
Don’t Forget Micronutrients
Vitamins and minerals support enzyme functions in your body. For instance, best vitamins for metabolism might include B-complex vitamins, which help convert food into usable energy. Coupled with adequate magnesium (e.g., via magnesium glycinate), you have a strong foundation for metabolic support.4
Finally, hydrate consistently. Water is crucial for nearly every bodily function. Even mild dehydration can slow down your metabolism. If you want to see how to burn more calories at rest, start with proper hydration—it’s a simple but sometimes overlooked step.
3. The Power of Exercise—Moving for Metabolic Health
Physical activity is one of the most effective ways to see immediate changes in your metabolic rate. If you’ve ever felt energized after a workout, you’ve experienced how exercise can naturally boost metabolism. But not all exercise is created equal when it comes to fueling calorie burn.
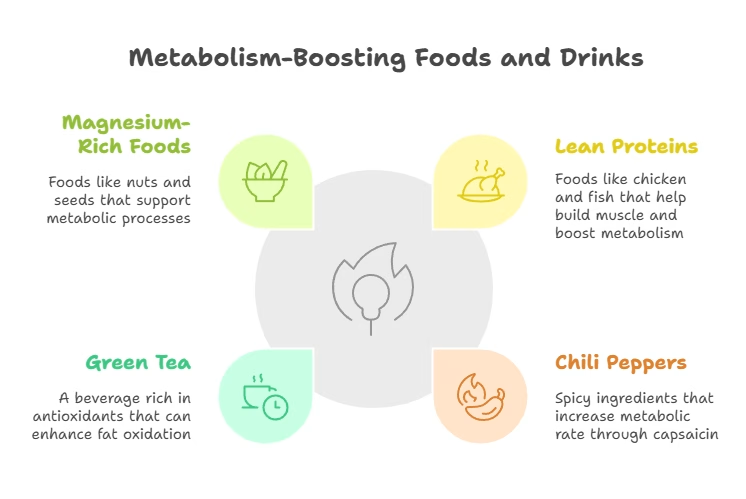
Strength Training for Metabolism
Muscle tissue is more metabolically active than fat tissue. The more muscle you have, the higher your basal metabolic rate. If you’re focusing on tips for increasing metabolic rate, consider adding resistance exercises like weightlifting or bodyweight training to your routine. Studies show that consistent strength training can help preserve or increase lean muscle, thereby enhancing how to burn more calories at rest (Harvard Health Publishing, 2020).
Interval Workouts and Cardio
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) alternates short bursts of intense exercise with rest or low-intensity intervals. It has been linked to increased metabolic rate even after your workout is done, a phenomenon called excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC). Similarly, steady-state cardio (like a brisk walk or jog) also contributes to daily calorie expenditure, though the after-burn effect is less pronounced than in HIIT.
Incorporate Daily Movement
Beyond structured workouts, simple actions like standing breaks during work, short walks, or taking the stairs can keep your body from slipping into idle mode. The concept of “non-exercise activity thermogenesis” (NEAT) highlights the importance of daily activities in calorie burning. So if you’re looking for ways to naturally boost metabolism, remember that every bit of movement adds up.
A unique insight: Try pairing strength training with brisk walks. This blend can create a sustained metabolic boost without overtaxing your system, making it accessible even if you’re short on time or new to exercise.
4. Sleep and Stress—Underrated Factors That Influence Metabolism
Most articles about how to increase metabolism mention exercise and diet first—and for good reason. But sleep and stress can quietly shape the bigger picture. If you’re not getting enough rest, or if your stress levels are sky-high, your body might struggle to maintain a healthy metabolic rate.
Sleep and Metabolic Rate
Lack of sleep is linked to hormonal imbalances, including changes in ghrelin and leptin, which regulate hunger. When you’re short on sleep, you may crave high-calorie foods and feel hungrier throughout the day. Over time, this can lead to weight gain and a sluggish metabolism (Mayo Clinic, 2021). Aim for seven to nine hours of quality sleep to support a healthy lifestyle for better metabolism.
Cortisol and Chronic Stress
Cortisol is the body’s primary stress hormone. In small bursts, cortisol helps you manage immediate stress. However, when stress becomes chronic, elevated cortisol levels may interfere with your metabolic rate and even encourage fat storage, especially around the midsection (WebMD, 2021). If you’re determined to figure out how to burn more calories at rest, managing stress might be just as crucial as lifting weights or tweaking your diet.
Practical Tips to Manage Stress
- Mindfulness or Meditation: Spending a few minutes each day in mindful breathing can lower cortisol levels.
- Physical Activity: Exercise helps release endorphins, which combat stress chemicals in the body.
- Social Support: Talking to friends, journaling, or seeking professional help can ease chronic stress.
A less-discussed perspective: Try pairing magnesium glycinate supplementation with mindful breathing exercises in the evening. Research suggests magnesium can promote relaxation, especially when combined with other stress-reduction techniques (Verywell Fit, 2022).
5. Meal Timing and Frequency—Does It Affect Metabolism?
You’ve likely heard the advice to eat small, frequent meals to “stoke the metabolic fire.” While some people find that strategy helpful, others do just fine on three square meals a day. The question is: does meal timing significantly impact how to increase metabolism?
The Thermic Effect of Food
Every time you eat, your body expends energy to digest and absorb nutrients. This is the thermic effect of food (TEF). The magnitude of TEF depends more on what you eat (protein tends to have a higher TEF) than on how often you eat. So, having six small meals might not necessarily boost your overall metabolic rate compared to three meals, assuming calorie totals remain the same.
Intermittent Fasting and Metabolism
Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained popularity. Some people find it helps with weight management and metabolic health. By restricting eating to a certain window, the body has more time in a fasted state, which may promote fat burning. However, what slows down metabolism in some cases could be an overly restrictive approach—leading to muscle loss if you’re not careful with protein intake and total nutrition.
Listening to Your Body
Ultimately, the best meal schedule is one that you can maintain comfortably, supports your overall nutrient needs, and aligns with your lifestyle. If smaller, more frequent meals help you manage hunger, go for it. If you prefer bigger, less frequent meals and still meet your calorie and nutrient goals, that’s fine too. The real secret to increasing metabolism safely lies in consistency, quality nutrition, and paying attention to how your body responds.
A unique angle: Experiment with “time-restricted eating” once a week and see how your energy levels and hunger cues shift. This can offer insights into whether intermittent fasting is a viable long-term tool for you.

6. Common Metabolism Myths Debunked
Understanding how to increase metabolism often involves filtering out myths and misinformation. Let’s tackle some of the most persistent ones:
Myth 1: “Spicy Foods Alone Will Skyrocket Your Metabolism”
While spicy foods like chili peppers can provide a slight boost, it’s usually not enough to create significant weight loss on its own. Real gains come from a comprehensive approach—exercise, balanced diet, and stress management.
Myth 2: “You Can’t Change Your Metabolism”
It’s true that genetics play a role, but you’re not stuck with the metabolism you were born with. Through regular strength training, proper hydration, quality sleep, and nutrient-rich meals, you can support your metabolic function.
Myth 3: “Only Intense Workouts Help”
Low-to-moderate activities, like daily walks, yoga, or climbing stairs, contribute to healthy lifestyle for better metabolism. The key is to stay active throughout the day, not just during one intense workout session.
Myth 4: “A Magic Supplement Will Solve Everything”
Certain supplements, like magnesium glycinate, can fill nutrient gaps, but no single pill will dramatically alter your metabolic rate if lifestyle factors are ignored.
What slows down metabolism more than anything else is prolonged inactivity and poor nutritional habits. So the best plan is always well-rounded: combine exercise, smart nutrition, adequate rest, and healthy stress management.
A unique perspective: Even mild fluctuations in daily routine can impact metabolism over time—for example, sitting for an extra hour each day for a week can subtly shift your overall calorie expenditure, reminding us that small changes do matter.
7. Tracking Progress—How to Know If You’re on the Right Path
When you’re implementing changes to learn how to increase metabolism, you might wonder: Is any of this working? While you can’t measure your metabolism directly at home, you can track clues that suggest your body’s energy use is evolving.
Body Composition Analysis
One of the most direct ways to gauge metabolic improvements is to monitor your body composition—the ratio of lean mass to fat mass. If your lean muscle mass is increasing and your body fat is decreasing, chances are your basal metabolic rate is on the rise. Tools like bioelectrical impedance scales or DEXA scans can offer insights, but even monitoring your waist circumference can help you spot trends.
Energy Levels and Mood
Improved energy and mood can indicate a healthy lifestyle for better metabolism. If you notice you’re feeling more alert during the day, or you’re able to handle physical tasks more easily, it could signal that your metabolism is more efficient.
Consistent Performance in Workouts
If you’re able to lift heavier weights or perform more reps over time, it suggests your muscle mass is growing. And what slows down metabolism less effectively than muscle loss? Gaining muscle usually means you’re revving up your basal metabolic rate, setting the stage for better calorie burning at rest.
A unique perspective: Journal about your daily habits (food intake, exercise, mood, stress levels) and look back every month. Patterns often reveal themselves more clearly over weeks than days, helping you fine-tune your approach if needed.
8. Personalized Approaches—One Size Doesn’t Fit All
The quest for how to increase metabolism can seem overwhelming, especially with so many tips out there. The truth is that everyone’s body is different. We have unique genetics, lifestyles, and preferences. Your friend might see success with intermittent fasting, while you might find consistency in three meals a day.
Tailoring Nutrition
If you have dietary restrictions or unique health conditions (like autoimmune disorders or diabetes), you may need to adjust your approach. Consult a registered dietitian to ensure your balanced diet meets your specific metabolic needs.
Exercise That Fits Your Lifestyle
A single parent might not have the same workout schedule as a college student. Tailor your exercise to your circumstances—maybe you do short, intense workouts, or maybe you spread out mini-workouts throughout the day. The best routine is the one you can stick to.
Stress Management That Resonates
Yoga works for some, while journaling or therapy works for others. The goal is to keep cortisol levels in check, so experiment with different methods until you find what truly helps you relax.
A unique takeaway: Consider cyclical approaches—alternate periods of higher-intensity routines with less-intense weeks. This strategy can prevent burnout and keep both your body and mind fresh. The main point is to listen to your body and adapt methods so they become a sustainable part of your life.
Quick Takeaways
- Build Lean Muscle: Strength training increases basal metabolic rate and helps you burn more calories at rest.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Protein-rich foods, coupled with essential vitamins and minerals (like magnesium glycinate), can support metabolic functions.
- Stay Hydrated: Even mild dehydration can reduce your metabolic efficiency.
- Manage Stress and Sleep: Chronic high cortisol and poor sleep can derail your metabolism.
- Stay Active All Day: Simple actions like frequent breaks, walks, or stairs can add up.
- Customize Your Plan: Everyone’s body is different, so tailor your nutrition and exercise to your lifestyle.
- Track Your Progress: Observe changes in energy, mood, and body composition to gauge improvements.
Conclusion
By now, you’ve seen that how to increase metabolism isn’t about quick fixes or miracle supplements. It’s about weaving together small, consistent habits that support your body’s natural processes. From building lean muscle and following a balanced diet to getting enough sleep and managing stress hormones like cortisol, every action contributes to a healthier, more efficient metabolic rate.
Understanding that you have control over many aspects of metabolism can be empowering. Rather than feeling stuck with “bad genes” or an “inherently slow” metabolism, you can take steps each day that, over time, lead to noticeable changes. The key is consistency and personalization. Not every strategy will work the same for everyone, and that’s okay. What matters is finding a sustainable routine that keeps you moving, well-fueled, and well-rested. In the long run, these foundational pieces will help ensure you’re not just burning more calories, but also feeling stronger, more alert, and better equipped to enjoy life. Keep exploring, keep experimenting, and watch how these changes gradually transform your energy, body composition, and overall health.
FAQs
- How long does it take to see changes in metabolism?
Results vary. Some people notice improvements in energy and body composition within a few weeks of consistent exercise and dietary changes. But a solid transformation in metabolic rate can take a few months, especially if you’re adding lean muscle. - Can a slow metabolism be genetic?
Yes, genetics do play a role in what slows down metabolism, but lifestyle factors can still make a significant impact. Strength training, balanced diet, and good sleep are powerful tools for most individuals. - Is intermittent fasting the best way to boost metabolism?
Intermittent fasting can work for some, but it’s not universally superior. The key to ways to naturally boost metabolism is finding a dietary pattern you can maintain long-term without nutritional gaps. - Do supplements like magnesium glycinate really help?
They can help fill nutrient gaps, especially if you’re low in magnesium. While magnesium glycinate is not a magic fix, it supports many biochemical processes, including those related to metabolism. - Will drinking more water actually increase my metabolic rate?
Consistent hydration helps the body’s metabolic processes run smoothly. While the calorie burn from drinking water alone is small, staying hydrated is essential for overall metabolic health.
Sources
- Healthline. (2022). Magnesium: Health Benefits and Recommended Intake.
- Medical News Today. (2021). Why Protein Matters for Metabolism.
- Harvard Health Publishing. (2020). Strength Training and Metabolic Rate.
- Mayo Clinic. (2021). Sleep and Metabolism.
- WebMD. (2021). The Effects of Cortisol on Metabolism.